
| Multiple ITSM Entry Points Last month we discussed several questions that are typical of an ITSM effort; where is the best place to begin, what is the best way to proceed, what are the expertise and resource issues, and what are some critical success factors. As we mentioned, the size, scope, and complexity of an ITSM effort is a long term strategy that has multiple entry points depending on unique customer requirements and maturity levels. However, some tactical areas are better starting points than others due to the size of the effort required, the benefits provided in the short term, and the strategic positioning provided. This month we will explore some of these useful ITSM starting areas, the effort involved, and the benefits provided. ITSM Effort Starting Points and Core Areas A Review of ITSM Effort Basics |
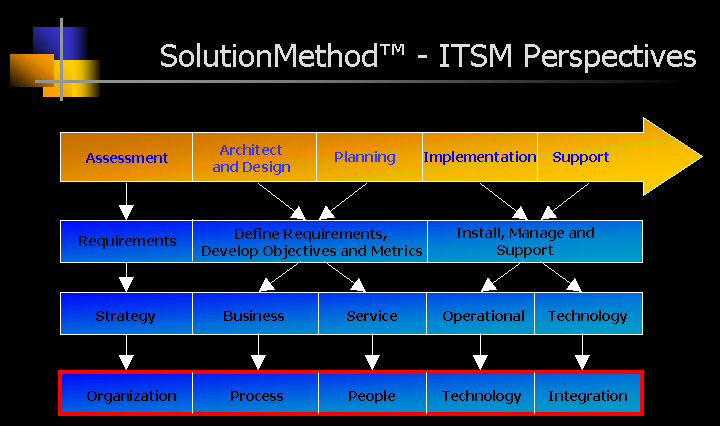
| Service Level Management as The Core of ITSM Encompassed within service level management are negotiating and documenting service level objectives and agreements, service level monitoring and reporting, and developing and maintaining a service catalog. Service Level Management is the process of managing the quality and quantity of a delivered IT service. It is an approach to delivering business critical IT services that focus on meeting agreed upon cost and performance targets developed and implemented in partnership with internal customers and embodied in service level agreements. Service Level Management is a "customer-focused" perspective within IT that reflects the need for customers of IT services to become a valued business partner. This customer focus embodies some of the following key transition elements for IT: • Viewing consumers of their services as "customers" instead of "users" • Expanding the traditional "inward" perspective to looking "outward" • Expanding the focus on technology to include a focus on process • Migration from isolated "ad hoc" processes to business focused, replicable IT processes • Addressing customer service requirements with "measured, accountable" IT processes instead of "best effort" • Expand service provisioning from "in house" to include a cost-justified balance between "in sourcing" and "outsourcing" • Develop and implement integrated, end-to-end business to IT processes to replace "silo" oriented, fragmented processes • Using repeatable processes to migrate from a reactive IT organization to proactive • Define and develop new service-oriented roles and responsibilities • Enhance the IT system skill set to include a customer-focused orientation Service Level Management within ITSM focuses on translating business and IT strategy into IT services, managing the service levels for those services, and putting in place continuous service improvement processes for these services. With this focus in mind, service level management plays a critical role through the development and use of service level objectives and agreements that provide the necessary metrics for measuring, assessing, managing, and reporting agreed upon service between IT and its customers. Some co-dependent areas linked with it are Availability, Capacity, Financial, and Performance Management. |
|
RL Consulting Announces New ITSM Tools and Workshops
Utilizing SolutionMethod™ proprietary questions and evaluation processes, RL Consulting employs 3 automated tools; ITSM Assessment Worksheet, ITSM ROI Worksheet, and ITSM Implementation Readiness Worksheet. |
| The Components of a Service Catalog The context of Service Level Management within an ITSM best practice infrastructure, a Service Catalog is more than just a descriptive inventory of application systems. The development of the service catalog is a critical first step in identifying and qualifying the types of services being provided. Beyond an inventory of applications, the business functions they support, and the technology architecture that supports it, the service catalog integrates service level objectives and agreements that have a business and customer service focus with financial metrics, if appropriate. Preferably it encompasses the 5 perspectives of people, process, technology, organization, and integration. It should be a published (an HTML format works well) and maintained. In this fashion it can be available for reference and actively used in the management of services. The Goal of Service Level Management Achieving ITSM service level management best practices will provide the following benefits: • An optimized, service focused organization • A well defined and effective set of tailored processes and methods that is supported enterprise-wide and is continuously improved • An integrated set of service metrics that are qualified and quantified being developed, documented, agreed upon, implemented, reported on, and managed to. These metrics encompass business requirements and the services provided to satisfy them |
White Papers: » SLA Description and Templates » Consolidation Questionnaires » Service Continuity Methods » Project Management Practices » Developing a Communication Plan » Data Management Process Service Briefs: » ITSM Maturity Assessment » Incident and Problem Management » Service Continuity » Config and Change Management » Service Level Management » Capacity Management » Availability Management » Release Management |
Additional Information
Visit www.itsm.info
to learn about ITSM, IT Infrastructure
Library (ITIL), and SolutionMethod™ (a
Policy Based ITSM Approach). In
addition, you can download free and
informative white papers,
questionnaires, and service briefs. This includes more in-depth information on the topics presented in this newsletter.
To learn how RL Consulting
can assist in achieving IT Service Management goals and our full range of solutions:
Contact us at RL_Consulting@itsm.info or phone us at 602-996-6830
* In the upcoming months this newsletter will contain important information concerning the various aspects of IT Service Management. If you no longer wish to receive this newsletter simply reply to this message with "REMOVE" in the subject line.
Volume 3 - May, 2002
This newsletter and the information contained herein is maintained by Rick Leopoldi and the property of RL Information Consulting LLC.